JS中的树形数据结构处理
前言
树形数据的遍历方式本质上是数据结构二叉树遍历的主要思想。所以以下遍历方式主要是广度优先遍历和深度优先遍历。
遍历方式:
-
广度优先遍历(广度优先搜索在二叉树上的应用:即层序遍历。)
即逐层地,从左到右访问所有节点。 -
深度优先遍历
- 前序遍历 - 遍历顺序:中左右: 1. 递归法; 2. 迭代法(压栈顺序:右左中)
- 中序遍历 - 遍历顺序:左中右: 1. 递归法; 2. 迭代法(压栈顺序:左中右)
- 后序遍历 - 遍历顺序:左右中: 1. 递归法; 2. 迭代法(压栈顺序:左右中)
遍历思想:迭代法 - 栈; 层序遍历 - 队列
相关处理方法
// 用于测试的树形数据
const treeData = [
{
id: "1",
name: "测试1",
pId: "0",
type: "group",
children: [
{
id: "11",
name: "测试11",
pId: "1",
type: "group",
children: [
{
id: "111",
name: "测试111",
pId: "11",
type: "group",
children: [
{
id: "1111",
name: "测试1111",
pId: "111",
},
{
id: "1112",
name: "测试1112",
pId: "111",
},
],
},
{
id: "112",
name: "测试112",
pId: "11",
children: [
{
id: "1121",
name: "测试1121",
pId: "112",
},
],
},
{
id: "113",
name: "测试113",
pId: "11",
},
],
},
{
id: "12",
name: "测试12",
pId: "1",
type: "group",
children: [
{
id: "121",
name: "测试121",
pId: "12",
},
],
},
{
id: "13",
name: "测试13",
pId: "1",
},
{
id: "14",
name: "测试14",
pId: "1",
},
],
},
{
id: "2",
name: "测试2",
pId: "0",
children: [
{
id: "21",
name: "测试21",
pId: "2",
children: [
{
id: "211",
name: "测试211",
pId: "21",
},
{
id: "212",
name: "测试212",
pId: "21",
},
],
},
{
id: "22",
name: "测试22",
pId: "2",
},
],
},
]
1. 查找当前节点
方法 1:层序遍历(广度优先遍历)
function getCurNode(data, key) {
const queue = JSON.parse(JSON.stringify(data))
while (queue.length) {
const len = queue.length
for (let i = 0; i < len; i++) {
const node = queue.shift()
if (node.id === key) {
return node
} else {
node.children && queue.push(...node.children)
}
}
}
return null
}
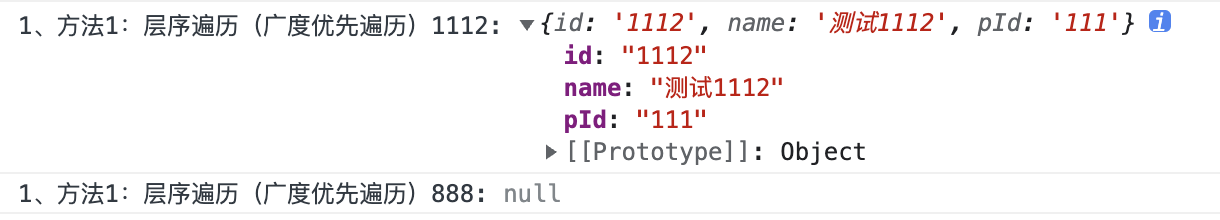
const curNode1 = getCurNode(treeData, "1112")
console.log("1、方法1:层序遍历(广度优先遍历)1112:", curNode1)
const curNode2 = getCurNode(treeData, "888")
console.log("1、方法1:层序遍历(广度优先遍历)888:", curNode2)
方法 2:递归
function getCurrentNode(data, key) {
let temp = null
for (let i = 0; i < data.length; i++) {
if (data[i].id === key) {
return data[i]
} else if (data[i].children?.length) {
const o = getCurrentNode(data[i].children, key)
if (o) return o
}
}
return temp
}
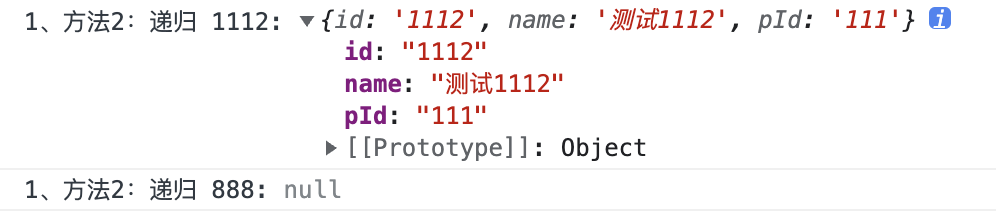
const currentNode1 = getCurNode(treeData, "1112")
console.log("1、方法2:递归 1112:", currentNode1)
const currentNode2 = getCurNode(treeData, "888")
console.log("1、方法2:递归 888:", currentNode2)
2. 获取当前节点及以下的所有节点 id
方法 1:层序遍历
function getChildrenId(data) {
const idArr = []
const queue = JSON.parse(JSON.stringify(data))
while (queue.length) {
const len = queue.length
for (let i = 0; i < len; i++) {
const node = queue.shift()
idArr.push(node.id)
node.children && queue.push(...node.children)
}
}
return idArr
}
const idArr1 = getChildrenId(treeData)
console.log("2、方法1:层序遍历", idArr1)

方法 2:递归
function getChildrenId2(data, idArr = []) {
data.forEach((el) => {
idArr.push(el.id)
el.children && getChildrenId2(el.children, idArr)
})
return idArr
}
const idArr2 = getChildrenId2(treeData)
console.log("2、方法2:递归", idArr2)

3. 判断所有后代节点中有无此节点中的一个
方法 1:层序遍历(广度优先遍历)
function judgeChildrenHad(data, keys) {
const queue = JSON.parse(JSON.stringify(data))
while (queue.length) {
const len = queue.length
for (let i = 0; i < len; i++) {
const node = queue.shift()
if (keys.includes(node.id)) {
return true
} else {
node.children?.length && queue.push(...node.children)
}
}
}
return false
}
const mark4 = judgeChildrenHad(treeData, ["11"])
console.log("3.方法1:层序遍历(广度优先遍历)mark4", mark4)
const mark5 = judgeChildrenHad(treeData, ["1121"])
console.log("3.方法1:层序遍历(广度优先遍历)mark5", mark5)
const mark6 = judgeChildrenHad(treeData, ["888"])
console.log("3.方法1:层序遍历(广度优先遍历)mark6", mark6)

方法 2:递归
function judgeChildrenHad2(data, keys) {
let mark = false
const fn = (data, keys) => {
for (let i = 0; i < data.length; i++) {
if (keys.includes(data[i].id)) {
mark = true
} else if (data[i].children?.length) {
fn(data[i].children, keys)
}
}
}
fn(data, keys)
return mark
}
// 判断 treeData后代节点中有无 测试1112(1112)节点
const mark1 = judgeChildrenHad2(treeData, ["1112"])
console.log("3. 方法2:递归 mark1", mark1)
// 判断 treeData后代节点中有无 测试1121(1121)节点
const mark2 = judgeChildrenHad2(treeData, ["1121"])
console.log("3. 方法2:递归 mark2", mark2)
// 判断 treeData后代节点中有无 测试888(888)节点
const mark3 = judgeChildrenHad2(treeData, ["888"])
console.log("3. 方法2:递归 mark3", mark3)

4. 树形数据扁平化
方法 1:层序遍历(广度优先遍历)
function treeToFlat(data) {
const queue = JSON.parse(JSON.stringify(data))
const result = []
while (queue.length) {
const node = queue.shift()
if (node.children?.length) {
queue.push(...node.children)
Reflect.deleteProperty(node, "children")
}
result.push(node)
}
return result
}
console.log("4、方法1:层序遍历(广度优先遍历)", treeToFlat(treeData))

方法 2:递归
function treeToFlat2(data) {
const result = []
data.forEach((item) => {
const obj = {
name: item.name,
id: item.id,
pId: item.pId,
}
result.push(obj)
if (item.children?.length) {
result.push(...treeToFlat2(item.children, item.id))
}
})
return result
}
const res1 = treeToFlat2(treeData)
console.log("4、方法2:递归", res1)

5. 扁平化数据转树形结构
方法 1:Map 对象
function flatToTree(data) {
const result = []
const itemMap = {}
for (const item of data) {
const id = item.id
const pId = item.pId
if (itemMap[id]) {
itemMap[id] = {
...itemMap[id],
...item,
}
} else {
itemMap[id] = { ...item }
}
const treeItem = itemMap[id]
if (!pId || pId === "0") {
result.push(treeItem)
} else {
if (!itemMap[pId]) {
itemMap[pId] = {
children: [],
}
}
if (!itemMap[pId].children) {
itemMap[pId].children = []
}
itemMap[pId].children.push(treeItem)
}
}
return result
}
const r = JSON.parse(JSON.stringify(res1))
r.unshift({
id: "999",
name: "yyyyy",
pId: "1",
})
const res2 = flatToTree(r)
console.log("5. 扁平化数据转树形数据结构 方法1:Map对象", res2)

方法 2:递归
function flatToTree2(data) {
const result = []
const fn = (arr, cArr, pId = "0") => {
for (let i = 0; i < arr.length; i++) {
const item = { ...arr[i], children: [] }
if (arr[i].pId === pId) {
cArr.push(item)
fn(arr, item.children, arr[i].id)
}
}
}
fn(data, result)
return result
}
const r2 = JSON.parse(JSON.stringify(res1))
r2.unshift({
id: "999",
name: "yyyyy",
pId: "1",
})
console.log("5. 扁平化数据转树形数据结构 方法2:递归", flatToTree2(r2))

6. 查找当前节点的父节点
方法 1:层序遍历(广度优先遍历)
function getParentNode(data, key) {
const queue = JSON.parse(JSON.stringify(data))
while (queue.length) {
const len = queue.length
for (let i = 0; i < len; i++) {
const node = queue.shift()
const childIdArr = (node.children || []).map((el) => el.id)
if (childIdArr.includes(key)) {
return node
} else {
node.children?.length && queue.push(...node.children)
}
}
}
return null
}
const pResult1 = getParentNode(treeData, "1111")
console.log("6、方法1:层序遍历(广度优先遍历) 1111: ", pResult1)
const pResult2 = getParentNode(treeData, "212")
console.log("6、方法1:层序遍历(广度优先遍历) 212: ", pResult2)
const pResult3 = getParentNode(treeData, "888")
console.log("6、方法1:层序遍历(广度优先遍历) 888: ", pResult3)

方法 2:递归
function getParentNode2(data, key) {
for (let i = 0; i < data.length; i++) {
if (data[i].children?.length) {
if (data[i].children.some((item) => item.id === key)) {
return data[i]
} else {
const temp = getParentNode2(data[i].children, key)
if (temp) return temp
}
}
}
return null
}
const pResult4 = getParentNode2(treeData, "1111")
console.log("6、方法2:递归 1111: ", pResult4)
const pResult5 = getParentNode2(treeData, "212")
console.log("6、方法2:递归 212: ", pResult5)
const pResult6 = getParentNode2(treeData, "888")
console.log("6、方法2:递归 888: ", pResult6)

7. 查找当前节点的所有直系祖先节点(例:当前节点:1111,所有祖先节点为:111,11,1)
function getAllParentNode(data, key) {
const arr = []
const fn = (data, key) => {
const p = getParentNode(data, key)
if (p && p.id) {
arr.push(p)
fn(data, p.id)
}
}
fn(data, key)
return arr
}
const pArr1 = getAllParentNode(treeData, "1121")
console.log("7、查找当前节点的所有祖先节点 1121:", pArr1)
const pArr2 = getAllParentNode(treeData, "212")
console.log("7、查找当前节点的所有祖先节点 212:", pArr2)

8. 获取树形数据的最深层级数字(深度)
方法 1:层序遍历(广度优先遍历)
function getDeepRank(data) {
let deepRank = 0
const queue = JSON.parse(JSON.stringify(data))
while (queue.length) {
const len = queue.length
deepRank++
for (let i = 0; i < len; i++) {
const node = queue.shift()
node.children?.length && queue.push(...node.children)
}
}
return deepRank
}
console.log("8、方法1:层序遍历(广度优先遍历):", getDeepRank(treeData))

方法 2:递归
function getDeepRank2(data) {
let deepRank = 0
const fn = (arr, num = 0) => {
for (let i = 0; i < arr.length; i++) {
let rank = num || num + 1
deepRank = Math.max(deepRank, rank)
if (arr[i].children?.length) {
fn(arr[i].children, rank + 1)
}
}
}
fn(data)
return deepRank
}
console.log("8、方法2:递归:", getDeepRank2(treeData))

9. 递归筛选符合条件的数据
function handleFilterData(data, arr = []) {
data.forEach((el) => {
if (el.type === "group") {
// 筛选条件
const newNode = {
...el,
children: [],
}
arr.push(newNode)
el.children?.length && handleFilterData(el.children, newNode.children)
}
})
return arr
}
console.log("9. 递归筛选符合条件的数据", handleFilterData(treeData))



