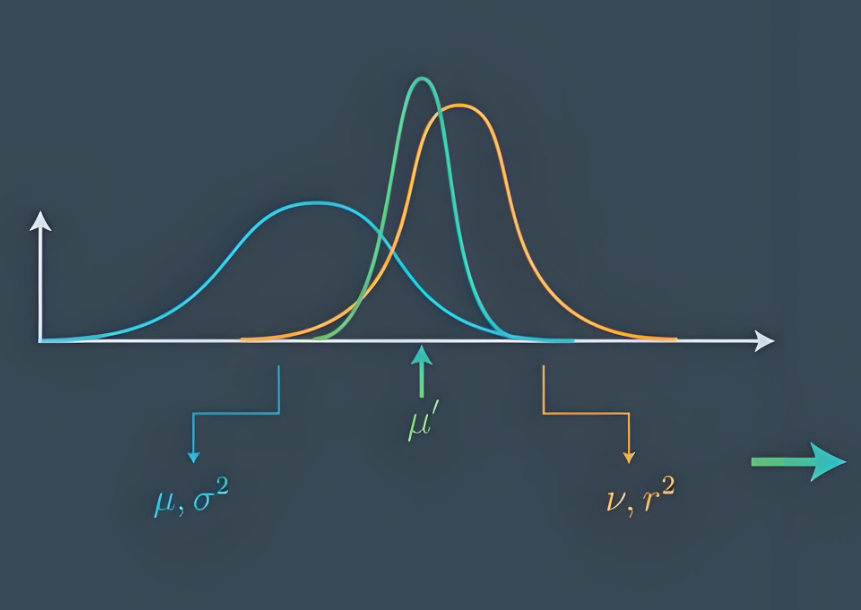
原理
卡尔曼滤波是一种用于线性动态系统的递归估计方法,它可以估计系统的状态,即使系统的过程和测量噪声是随机的和不确定的。
步骤
预测阶段: 根据前一时刻的状态估计和控制输入预测当前时刻的状态。
更新阶段: 使用当前的测量数据更新预测的状态,以得到更准确的估计。
状态转移方程: 描述系统的动态过程。
观测方程: 描述测量值与状态的关系。
应用
卡尔曼滤波被广泛应用于导航、跟踪和信号处理等领域,尤其适合处理噪声较大的动态系统。
代码实现
public class KalmanFilter {
private double q; // process noise covariance
private double r; // measurement noise covariance
private double x; // estimated value
private double p; // estimation error covariance
private double k; // kalman gain
public KalmanFilter(double processNoise, double measurementNoise, double estimatedError, double initialValue) {
this.q = processNoise;
this.r = measurementNoise;
this.p = estimatedError;
this.x = initialValue;
}
public void update(double measurement) {
// Prediction update
p = p + q;
// Measurement update
k = p / (p + r);
x = x + k * (measurement - x);
p = (1 - k) * p;
}
public double getValue() {
return x;
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
KalmanFilter kf = new KalmanFilter(1, 1, 1, 0);
double[] measurements = {1, 2, 3, 4, 5};
for (double measurement : measurements) {
kf.update(measurement);
System.out.println("Estimated value: " + kf.getValue());
}
}}
class KalmanFilter:
def __init__(self, process_noise, measurement_noise, estimated_error, initial_value):
self.q = process_noise
self.r = measurement_noise
self.p = estimated_error
self.x = initial_value
def update(self, measurement):
# Prediction update
self.p = self.p + self.q
# Measurement update
k = self.p / (self.p + self.r)
self.x = self.x + k * (measurement - self.x)
self.p = (1 - k) * self.p
def get_value(self):
return self.x
kf = KalmanFilter(1, 1, 1, 0)
measurements = [1, 2, 3, 4, 5]
for measurement in measurements:
kf.update(measurement)
print("Estimated value:", kf.get_value())
class KalmanFilter {
constructor(processNoise, measurementNoise, estimatedError, initialValue) {
this.q = processNoise;
this.r = measurementNoise;
this.p = estimatedError;
this.x = initialValue;
}
update(measurement) {
// Prediction update
this.p = this.p + this.q;
// Measurement update
const k = this.p / (this.p + this.r);
this.x = this.x + k * (measurement - this.x);
this.p = (1 - k) * this.p;
}
getValue() {
return this.x;
}}
const kf = new KalmanFilter(1, 1, 1, 0);
const measurements = [1, 2, 3, 4, 5];
for (const measurement of measurements) {
kf.update(measurement);
console.log("Estimated value:", kf.getValue());}
using System;
public class KalmanFilter {
private double q; // process noise covariance
private double r; // measurement noise covariance
private double x; // estimated value
private double p; // estimation error covariance
private double k; // kalman gain
public KalmanFilter(double processNoise, double measurementNoise, double estimatedError, double initialValue) {
this.q = processNoise;
this.r = measurementNoise;
this.p = estimatedError;
this.x = initialValue;
}
public void Update(double measurement) {
// Prediction update
p = p + q;
// Measurement update
k = p / (p + r);
x = x + k * (measurement - x);
p = (1 - k) * p;
}
public double GetValue() {
return x;
}
public static void Main(string[] args) {
KalmanFilter kf = new KalmanFilter(1, 1, 1, 0);
double[] measurements = { 1, 2, 3, 4, 5 };
foreach (double measurement in measurements) {
kf.Update(measurement);
Console.WriteLine("Estimated value: " + kf.GetValue());
}
}}
说明
过程噪声 (q):系统的内在不确定性。
测量噪声 (r):传感器的不确定性。
估计误差 (p):对当前状态的不确定性估计。
初始值 (x):卡尔曼滤波器开始估计的初始状态。
这些示例假设了一维线性系统。实际应用中可能需要根据具体系统的动态特性进行调整。对于多维系统,状态和协方差矩阵的维度和计算将更加复杂。